6 Ways to Elevate the Impression You Make at Work Jul 02, 2025

Tips to Win More Rummy Games Jun 24, 2025

Effective Campaigns That Drive Fundraising Results Apr 21, 2025




Hernando County: The Next Stop in Florida's Commercial Real Estate Market Journey by Lawrence Todd Maxwell of MX Properties, Inc




The Importance of Employee Relations Dec 18, 2024
Why You Need a Brain Injury Lawyer in Toronto Dec 04, 2024
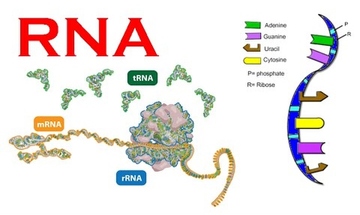
Why Total RNA extraction is important in bio-genetics.
Aug 28, 2018 08:50
With the increasing number of hereditary diseases and gene related illnesses, scientists have buried themselves in research and experiments to try and comprehend them. This science of genetics includes full analysis of the genetic markers, proteins and alignment of genes in individuals. Among the things studied is the RNA. However, RNA is not as long lived as the DNA as it is subject to degradation by the RNases enzymes. It was therefore important that scientists develop a way of total RNA extraction that realizes viable RNA samples for study and analysis.
If you are looking for a quality supplier of total RNA then visit the website here.
Importance of Total RNA extraction.
The RNA plays a crucial role in gene manifestation and expression, and thus the comprehension of most of the biological processes. Total RNA comprises of both mRNA and miRNA. The former spells out what the manifestation of the gene will be like, and the miRNA is responsible for silencing such. The miRNA is responsible for causing many genetic diseases including Huntington's Disease and Myotonic Dystrophy. RNA analysis is therefore crucial if scientists are to study these disorders and find corrections to them.
Total RNA extraction is therefore necessary in molecular experiments like digital PCR, array analysis and RNA sequencing. Extracted RNA reveals crucial information about gene structure, processes and interaction. They also reveal behavioral outcomes of specific cells when subjected to certain conditions and environments.
How to perform the RNA extraction.
Since the RNA have very short life spans compared to DNA, it would be wise to firstly paralyze the degrading enzymes but carefully not to damage the RNA. This is achieved using RNase inhibitors. There are several ways of total RNA extraction, each of which realizes a different composition and distribution of RNA.
#1. Direct Lysis
This non-purification technique requires addition of a lysis chemical to the sample and leaving the sample for a while so that the nucleic acids can stabilize. Downstream analysis is then performed to collect the RNA sample. This method is both fast and efficient even for small samples.
#2. Organic Method.
This is the basic and the standard method. It requires homogenization of the collected sample in a phenol based solution and then centrifuging it. The aqueous sample differentiates into three layers, only the top most layer is selected as it is the one that contains the RNA. A precipitation and dehydration using alcohol yields a proper RNA extract for study. This process is however laborious and uses potentially harmful chlorinated chemicals.
#3. Spin basket way.
This method is almost fully automated and requires lysis of the sample in guanidine salts, which are RNase inhibitors. This is followed by addition of other chemicals to precipitate the RNA extract after centrifugation into a tube through a membrane. This method however yields an extract that has large nucleic acids, which are not required.
#4. Extraction using magnetic particles.
This method involves introducing magnetic particles into an already lysed sample (using RNase inhibitors) and then applying a magnetic field. The particles have a shell that adheres required particles (the RNA molecules). Once the magnetic field is taken away, the precipitation can be washed and the magnetic particles easily removed. This realizes a RNA extract that is simple and fast in preparation.

Source
Making a positive impression at work is getting more important. This is partly because you don't actually go to work as often anymore thanks to hybrid working. So the impression you give in shorter stretches of time travels a lot further. The way you present yourself at work can actually influence your career trajectory, shaping perceptions and opening doors to new opportunities. Read more
Making a positive impression at work is getting more important. This is partly because you don't actually go to work as often anymore thanks to hybrid working. So the impression you give in shorter stretches of time travels a lot further. The way you present yourself at work can actually influence your career trajectory, shaping perceptions and opening doors to new opportunities. Read more
LIFESTYLE
Jul 02, 2025 10:41

Many people love a good game of Rummy. It's not all down to fate – winning in Rummy demands skills, strategies, and sound decisions. Whether you're learning for the first time or playing regularly, knowing a few essential tips can help you win more games. Read more
LIFESTYLE
Jun 24, 2025 10:40

Our lifestyle choices – the daily routines and decisions we make regarding how we live – have a remarkable effect on everything from our physical and mental wellbeing to our relationships and even our bank account. It's not all about being "healthy" in the picture-perfect, Instagram-friendly world. It's about building a rich life that allows you to flourish. Read more
LIFESTYLE
Jun 05, 2025 10:54
Copyright © Fooyoh.com. All rights reserved. User Agreement | Privacy Policy | Contact us
| Advertising
| About us
| Careers