5 factors that affect PCB Thermal Management
Jul 05, 2017 07:39
PCB Thermal Management is basically the PCB’s process of thoroughly releasing heat generated by high power designs or high thermal conductivity while controlling coefficients of thermal expansion. Without this important process, electronics would easily burst into flames due to overheating. The heat generated in PCBs originates from current flowing through the board and components.
Heat vias are channels which the PCB uses to radiate off any unwanted heat. These heat paths effectively direct heat energy away from the PCB without coming into contact with vital components. Effective thermal management ensures PCB components serve for lengthy durations without requiring repairs.
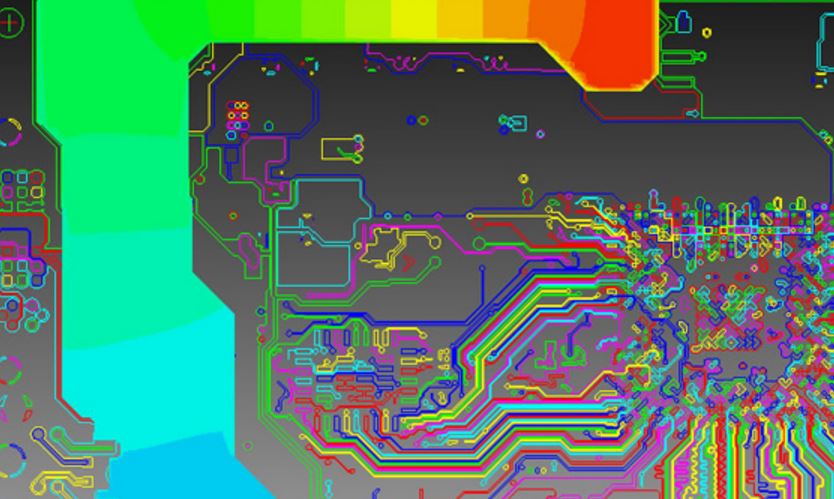
The list below highlights 6 factors which negatively affect your PCB’s ability to effectively dissipate excess heat.
Follow this link to receive additional PCB Thermal Management tips.
Heat vias are channels which the PCB uses to radiate off any unwanted heat. These heat paths effectively direct heat energy away from the PCB without coming into contact with vital components. Effective thermal management ensures PCB components serve for lengthy durations without requiring repairs.
The list below highlights 6 factors which negatively affect your PCB’s ability to effectively dissipate excess heat.
1. Insufficient space between electrical components in the PCB
Flaws in your initial PCB design can lead to poor space management where components are crowded rather than well spaced. In an effort to load up a PCB with a wide array of capabilities, electrical designers may incorporate many components on a single PCB. An overcrowded PCB has very little allowance for heat vias hence any radiated heat from various components ends up accumulating.2. Using aged PCB components
Some people believe old is gold but when it comes to designing PCBs, it’s wise to use new electrical components. Electrical parts contained in a PCB usually have limited life spans for effective use. It would be pointless to repair worn out components since their advanced wear and tear makes them extremely vulnerable to damage. Using old resistors for a new PCB may cause short circuits since resistance to current diminishes with time.3. Using faulty PCB parts
In an effort to minimize production costs, electrical engineers and manufacturers will invest in the cheapest products available in the market. Sometimes, cheap ends up being expensive due to frequent breakdowns which demand costly repairs. It is wrong to use components with frayed wires since they can easily short circuit or hinder effective current supply to certain components. Faulty capacitors may rupture due to inability to effectively release excess heat.4. Significant changes in external environment
Relocating to a new premises situated in a totally different climate may negatively affect your PCB’s ability to manage excess heat. Operating electronics in a high-temperature zone causes your PCB to heat up frequently since a lot of heat travels from the environment to the components via conduction. In this situation, the PCB receives more heat than the amount released through heat vias. Any moisture trapped within the components in this extreme weather condition accelerates rusting.5. Dust
The fan contained in a computer’s motherboard helps to regulate the PCB’s temperature through blowing away hot air trapped within the CPU. Dust that’s been left to accumulate over weeks or months inside the CPU ends up clogging heat vias on the PCB. The dust particles also hinder the fan from effectively spinning hence limits the amount of cool air flowing into dissipating unwanted heat.Summing it up
Adhering to the manufacture's product guide will enable your PCB to serve you longer. It's always important to ask your manufacturer for advice on how to maintain an optimum temperature for your PCB.Follow this link to receive additional PCB Thermal Management tips.